Howe Industries is developing a pulsed plasma rocket (PPR) capable of producing 100,000 N of thrust with a specific impulse of 5,000 seconds, advancing space travel by enabling faster and safer manned missions to Mars and beyond. It promises to start a revolution. (Artist's concept) Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Howe Industries' PPR has the potential to transform space exploration with its high thrust and specific impulse, enabling faster exploration. Mars Reinforced shielding ensures mission and safe transportation.
The future of space civilizations depends on moving both cargo and humans efficiently and quickly. Because space travel involves very long distances, spacecraft must reach high speeds to successfully complete a mission. Therefore, a propulsion system that generates high thrust with high specific impulse is essential. However, such technology is currently not available.
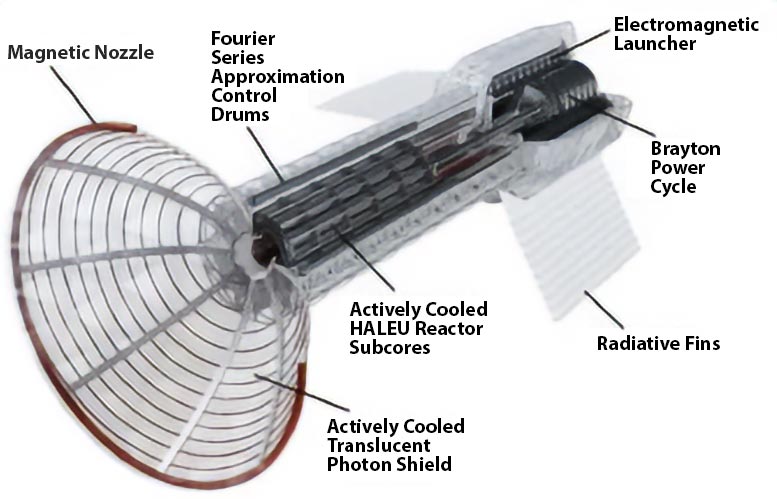
A simplified image of the PPR system.Credit: Brianna Clements, editor
Howe Industries is currently developing a propulsion system capable of producing up to 100,000 N of thrust at a specific impulse (Isp) of 5,000 seconds. Pulsed plasma rockets (PPR) are originally derived from the pulsed fusion concept, but are smaller, simpler, and more affordable.
The superior performance of PPR, combining high Isp and high thrust, has the potential to revolutionize space exploration. Due to the high efficiency of this system, a manned mission to Mars can be completed within just two months. Alternatively, PPR could allow the transport of much heavier spacecraft equipped with shielding against galactic cosmic rays, thereby reducing crew exposure to negligible levels.
The system can also be used for other long-range missions, such as missions to the asteroid belt and 550 AU locations where the focus of the Sun's gravitational lens is taken into account. PPR enables a whole new era in space exploration.
NIAC's Phase I research focused on large, heavily shielded vessels to transport humans and cargo to Mars for the development of a Mars base. Key topics include evaluating the neutronics of the system, designing the spacecraft, power system, and necessary subsystems, analyzing magnetic nozzle functionality, and determining PPR trajectories and benefits. Phase II builds on these assessments and further advances the PPR concept.
In Phase II, we plan to:
- Optimize engine design to reduce mass and increase Isp.
- Run proof-of-concept experiments for key components
- Complete the ship design for a manned mission to Mars


